Request a No-Cost Consultation
Toll Free: (888) 770-0004
Phone: (303) 770-7078
Request a No-Cost Consultation
Toll Free: (888) 770-0004
Phone: (303) 770-7078
A right to receive fixed, periodic payments, either for life or for a term of years.
Johann Gutenberg, inventor of the printing press, received an annuity, for a time, from the city of Mainz.
The largest annuity system today is the Social Security monthly retirement benefits system. (www.ssa.gov)
An annuity is a contract with an insurance company. With an annuity, the insurance company promises to pay you income on a regular basis for a period of time you choose -including the rest of your life.
Key takeaway: an annuity is a contractual agreement between you and an insurance company. The insurance company promises you X if you abide by Y.
**Each type of annuity has various features and options to choose from.
Annuities have traditionally been sold by insurance agents who were paid an upfront commission for the annuity sale.
Variable annuities added a twist, in such that advisors selling these products not only had to have an insurance license but also a Series 6 securities license, as variable annuities were deemed a security.
Commissioned Based Annuities
The agent is typically paid a large, one-time up-front commission from the insurance company. The purchaser of the annuity has a surrender charge that makes it difficult to move out of the annuity without incurring a fee. It is common to see a surrender charge that is 10-years long. An example is as follows:
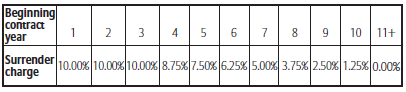
Other annuity contracts exist with very long surrender charges, such as an 18-year surrender charge period. However, be careful and do your due diligence. It is unwise to purchase one of these products. Confirm the surrender schedule is what your contract states.
Commission based variable annuities are known to have very high expenses. Be sure to do your homework.
Fee-Based Annuities
Fee-based annuities are a newer version of annuities that are designed for the fee-based, fiduciary advisor.
Fee-based advisors have to comply with either Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or State Securities Department rules and guidelines.
The advisor adds their advisory fee to the annuity just as they do with any other investment account they would manage on your behalf.
Benefits of a fee-based annuity are:
At Kompass Financial Advisors, as fiduciary advisors, we mostly use fee-based annuities, but there are situations where a commission-based annuity may be the more attractive option.
The size and financial ratings of the company are critical for their ability to deliver on their contractual obligations to their annuity contract holders.
Financial ratings examples are as follows:
AM Best: A++, A+, A, A-, B++, B+
Standard & Poor: AAA, AA+, AA, AA-, A+, A-
Moody’s: Aaa, Aa1, Aa2, Aa3, A1, A2, A3
Fitch: AAA, AA+, AA, AA-, A+, A, A-
COMDEX Rating, a composite of the above stated as a percentile against all companies.
Our goal is to use insurance companies that have a COMDEX rating in the 90th percentile of all insurance companies.
Do not simply take an insurance agent’s word that the company has good ratings. Understand the ratings system and obtain the ratings of each company you are considering. Do your due diligence, and of course, we can help you.
Qualified Annuities:
Non-Qualified Annuities:
**Always consult with a tax professional regarding the tax implication of purchasing an annuity and taking future distributions.
Do not hesitate to give us a call for help.